OpticalTableRobot
From HacDC Wiki
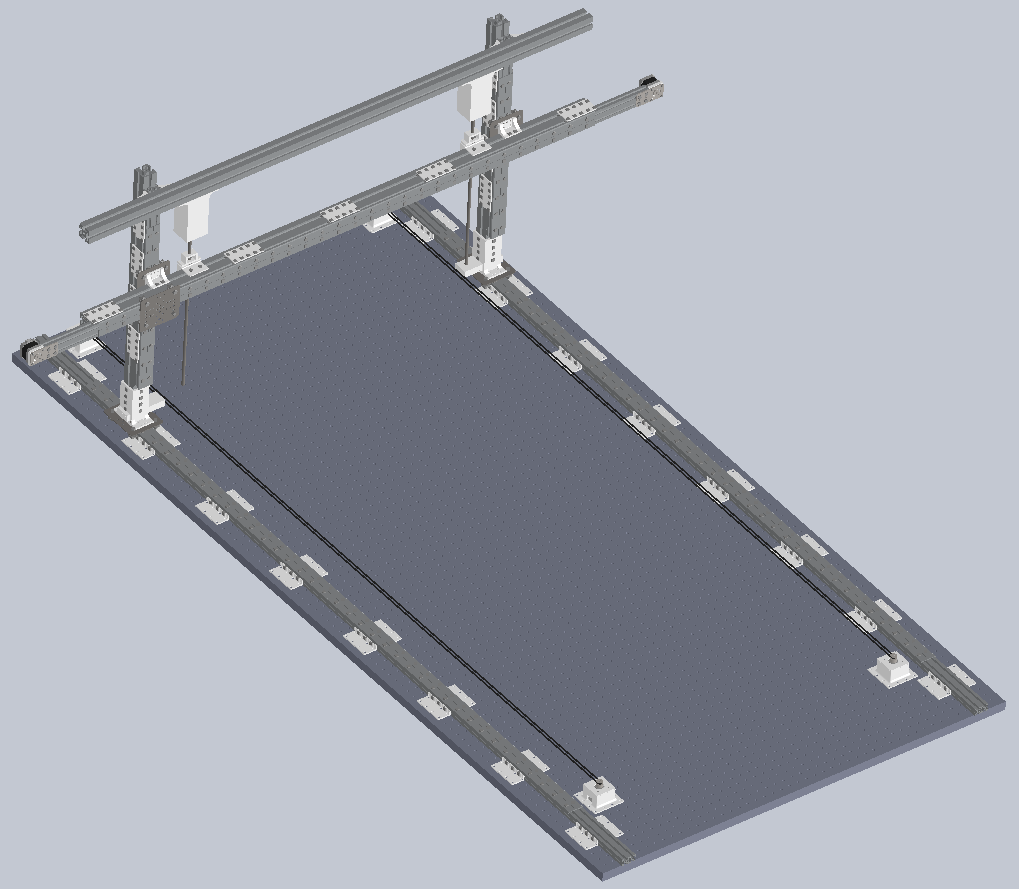
Multi-tool CNC platform in progress atop the optical table to enable ultra-precise fabrication on a massive scale. Derived from, and tool-compatible with, FlexReplicator.
This is the kind of machine one might use to 3D print large herringbone power transmissions for lost PLA casting, or carry out a VLSI production run.
Status
Funding available, design mostly complete, construction imminent.
Documentation
Design hosted on github.
Tools
Extruders
In progress. Works just like any other 3D printer. Plan on at least two nozzles, one for high-precision (<0.35mm), one for high-speed (>1mm).
Mill
In progress. Standard 120V AC drill, connected to control circuitry by SSR.
UV Laser Cutter
In progress. Planned as >2W and <1u focal spot.
VLSI Projection Lithography
Modified (ultraviolet) DLP projector and camera mounted to microscope, used for high-resolution patterning. Absolute accuracy (inter-frame) is expected to be ~2um, while relative accuracy (intra-frame) is expected to be <0.5um, scalable down to diffraction-limited performance.
Casting
Direct metal printing thus far is either highly expensive, low-strength, or both. Compromise is to 3D print a plastic (PLA) part, then cast it to metal. Besides low cost, this process can be used to achieve parts traditionally infeasible, like pre-assembled herringbone-gear power transmissions.
Pricing
As with other HacDC tools, operators are asked to pay for consumables used only for heavy usage. However, this machine can easily consume an entire a few hundred dollars of filament in one job...
Safety
Usual safety precautions apply. Additionally, open operation of a Class 4 laser demands eye protection for anyone in the room. Catastrophic retina damage will occur instantly upon viewing the projected spot, which is no less hazardous than direct beam viewing. This is especially true for lasers with a <10um wavelength (ie. non-CO2, eg. ultraviolet).
Upgrades
Once the basic platform has been deployed, simple upgrades may be applied if necessary. These may be particularly relevant to edge cases like CNC milling or VLSI patterning. However, these upgrades involve tradeoffs (ie. inertia, friction, cost, etc), and should only be applied upon discovery of a clear requirement.
Relative Accuracy (Vibration)
- Multiple Z-Axis gantries.
- Additional Z-axis actuators.
- Z-axis threaded rod stabilizers.
- Interferometric linear optical encoders.
Maximum Force
- Vectran rope timing belt replacements.
- Larger stepper motors.
- Combined X/Y actuators. Threaded rod and pulley.
Structural
- Metal cast replacements for 3D printed brackets (particularly gantry 'boots').